Supplemental ketones in the context of fasting | Rhonda Patrick
Get the full length version of this episode as a podcast.
This episode will make a great companion for a long drive.
The BDNF Protocol Guide
An essential checklist for cognitive longevity — filled with specific exercise, heat stress, and omega-3 protocols for boosting BDNF. Enter your email, and we'll deliver it straight to your inbox.
During ketogenesis, the metabolic pathway in which organisms produce ketones, the body breaks down fatty acids to use as fuel. The primary ketones used by the body for energy are acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate. Clinical data suggest that taking supplemental ketones during fasting increases blood levels of ketones but decreases levels of free fatty acids, indicating that the body is no longer relying on stored fatty acids. Although exogenous ketones provide a ready source of energy, their use might interfere with weight loss. In this clip, Dr. Rhonda Patrick describes the effects of endogenous ketones on fat metabolism during a fast.
[Mike]: You talked about ketones a bit in that last answer. So let's move on to a question about ketones from Austin. "Will consumption of exogenous ketones disrupt a fasting state? And I know that there's been a lot of work in producing ketone supplements. So that's the question I think is, will that disrupt the fat? "
[Dr. Patrick]: It's certainly a question that I've had myself. I've actually tried a beta-hydroxybutyrate, ester. So beta-hydroxybutyrate is the major circulating ketone body that's generated when your body starts to go into ketogenesis. A lot of things do happen when you're fasting and that's one of them. So basically, it takes anywhere between, you know, 12 to 36 hours for your liver to deplete the glycogen. And once that's depleted, what ends up happening is you immobilize fatty acids from your adipose tissue. They go to the liver and they're actually used to make ketone bodies. So you're oxidizing the fatty acids now using them to make ketone bodies like beta-hydroxybutyrate. Those ketone bodies can then be used as an alternative energy source themselves.
[Mike]: Which is incredible. I mean, just on that point, the fact that, you know, the analog I've heard is, you know, you basically turning your body from a, you know, burning gas to diesel. It's like a completely different fuel glucose to ketones. It's amazing that our bodies can even do that. And in some ways, you know, it's a preferred fuel for different organs in our bodies, right?
[Dr. Patrick]: It seems as though it might be. It certainly seems to be metabolically efficient. You know, so it takes less energy to use a ketone body compared to glucose. So it's energetically favorable in that sense, which is nice.
[Mike]: Sound like it doesn't really interrupt a fast and sort of part of the natural...
[Dr. Patrick]: Well, so let me, so I'll let me continue. So that was the natural phenomena I was explaining you, right?
[Mike]: Okay. Got it. Got it.
[Dr. Patrick]: Now, what ends up happening, so there's been about five clinical studies that I've read that have... They're most clinical studies with exogenous ketone esters .
[Mike]: And just for the audience, exogenes meaning not produced in the body. You're taking it externally.
[Dr. Patrick]: Exactly. You're taking a like a supplemental form of it. Yeah. Thanks for clarifying that. So the exogenous ketone esters that are taken, basically, a lot of the studies that have been done have been looking in the context of like athletic performance. But they also look at other metabolic parameters, which is interesting because that's kind of where you can find some of this data, if you look carefully. And within these five studies, there have been, it seems to be that what's been shown is that the exogenous consuming, for example, the exogenous beta-hydroxybutyrate, the supplemental beta-hydroxybutyrate ester, it ends up, it increases the blood levels of beta-hydroxybutyrate pretty high.
But it also seems to decrease circulating free fatty acids, which suggests you're not immobilizing fatty acids from your adipose tissue to be used to make your own, which means you may not be getting the benefit of what you would call a fat loss. Right. And that's a regulatory loop that occurs in the body. So it, you know, when your beta-hydroxybutyrate levels get high enough, you know, your body says, "Okay, we don't need to make any more of these." So it stops the immobilizing, what's called lipolysis, the cutting of the fatty acids from the adipose tissue, right?
[Mike]: Interesting.
[Dr. Patrick]: So your body's stopping you from making too much, right? So that does seem to happen. But then again, the exogenous ketone esters don't last for that long. And if you're exercising or doing physical activity, it's dose-dependent. So the more active you are, the quicker you use up those ketone bodies.
[Mike]: Yeah. It's interesting because you know, I know that when I'm practicing fasting, which gets my ketones way up, and then I'm doing a ketogenic diet, which does the same thing. And then, I go for a big workout, I'll come back and measure my ketone bodies and they're way down. And I guess it's because I've been using my ketones for during the workout.
[Dr. Patrick]: For energy. Yeah, exactly what happens. So that's kind of my one caveat that I would be aware of with consuming the beta-hydroxybutyrate supplemental esters or salts if you want. But salts don't work that well.
A good point is that they've also been shown consuming the exogenous beta-hydroxybutyrate has been shown in humans to prevent the use of amino acids from muscle. So it stops. And which also is, you know, makes sense during a prolonged fast, your body has mechanisms at play that help prevent you from, you know, using muscle, using proteins and amino acids from your muscle as energy. And one of those is that, you know, the ketone bodies prevents that from happening.
So that's a good thing. But so there's a trade-off, potentially. And again, this is something that, you know, I don't know how much of a difference it makes, but it's something to keep in mind.
- [Mike]: Yeah. And if you're an athlete and you're needing fuel, maybe you're a better candidate than someone that's just looking for purely metabolic body-based ketone production. And that's a maybe, but it's a factor.
A chemical produced in the liver via the breakdown of fatty acids. Beta-hydroxybutyrate is a type of ketone body. It can be used to produce energy inside the mitochondria and acts as a signaling molecule that alters gene expression by inhibiting a class of enzymes known as histone deacetylases.
A molecule composed of carboxylic acid with a long hydrocarbon chain that is either saturated or unsaturated. Fatty acids are important components of cell membranes and are key sources of fuel because they yield large quantities of ATP when metabolized. Most cells can use either glucose or fatty acids for this purpose.
A highly branched chain of glucose molecules that serves as a reserve energy form in mammals. Glycogen is stored primarily in the liver and muscles, with smaller amounts stored in the kidneys, brain, and white blood cells. The amount stored is influenced by factors such as physical training, basal metabolic rate (BMR), and eating habits.
A metabolic pathway in which organisms produce ketones. Ketogenesis occurs primarily in the mitochondria of liver cells via the breakdown of fatty acids and ketogenic amino acids. Insulin is the major hormonal regulator of ketogenesis; however, glucagon, cortisol, thyroid hormones, and catecholamines can induce greater breakdown of free fatty acids, thereby increasing the substrates available for use in the ketogenic pathway. The primary ketones used by the body for energy are acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate.
A diet that causes the body to oxidize fat to produce ketones for energy. A ketogenic diet is low in carbohydrates and high in proteins and fats. For many years, the ketogenic diet has been used in the clinical setting to reduce seizures in children. It is currently being investigated for the treatment of traumatic brain injury, Alzheimer's disease, weight loss, and cancer.
Molecules (often simply called “ketones”) produced by the liver during the breakdown of fatty acids. Ketone production occurs during periods of low food intake (fasting), carbohydrate restrictive diets, starvation, or prolonged intense exercise. There are three types of ketone bodies: acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone. Ketone bodies are readily used as energy by a diverse array of cell types, including neurons.
Attend Monthly Q&As with Rhonda
Support our work
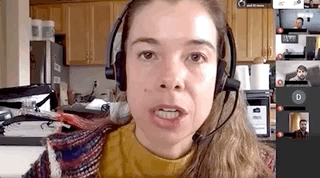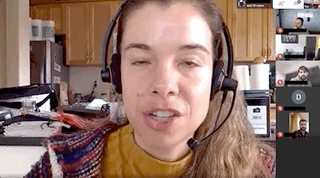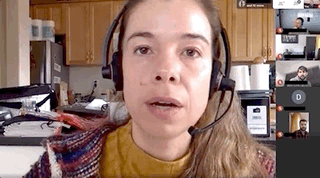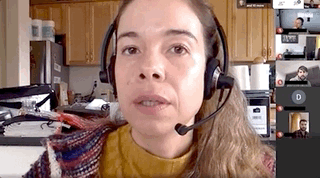
The FoundMyFitness Q&A happens monthly for premium members. Attend live or listen in our exclusive member-only podcast The Aliquot.
Fasting News
- Alternate-day fasting outperforms other intermittent fasting methods in weight loss and cholesterol reduction, according to a systematic review and meta‐analysis.
- Intermittent fasting three nonconsecutive days per week coupled with regular exercise promotes more weight loss than daily calorie restriction.
- Fasting-based dietary strategies, including intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating, show slight superiority over calorie restriction for promoting weight loss and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Cyclic fasting-mimicking diet in cancer treatment: Preclinical and clinical evidence
- Mild intermittent fasting can have a surprisingly negative effect on immunity: skipping breakfast led to a 90% drop in white blood cell count.





