The Phospholipid Brain-DHA Advantage
The BDNF Protocol Guide
An essential checklist for cognitive longevity — filled with specific exercise, heat stress, and omega-3 protocols for boosting BDNF. Enter your email, and we'll deliver it straight to your inbox.
Dr. Rhonda Patrick discusses the differences between different forms of DHA in terms of bioavailability and transport into different cells. She talks about why a specific type of DHA (DHA in phosphatidylcholine) is more readily transported into the brain because it forms DHA-lysophsophatidylcholine. Krill oil and salmon roe both have a slightly higher concentration of DHA-lysophosphatidylcholine. She also talks about astaxanthin, a carotenoid that is unique to krill oil, and has potent antioxidant activity and prevents the oxidation of DHA and EPA.
-
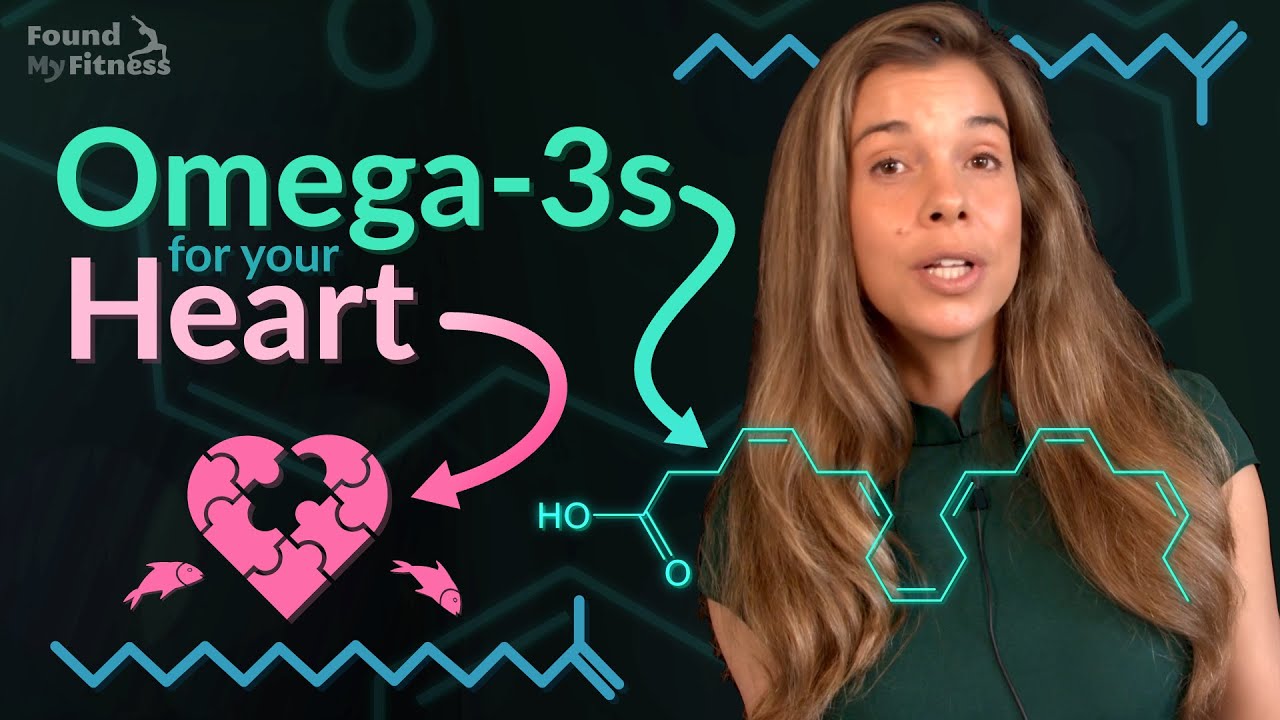
What are omega-3 fatty acids?
-
-
The benefits of consuming omega-3 fatty acids.
-
Three characteristics that differentiate krill oil from fish oil.
-
Bioavailability of krill vs fish oil.
-
-
-
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid effective in sequestering oxidative species.
The death rate from all causes of death for a population in a given time period.
The extent and rate at which drugs or other substances, such as plant-based dietary compounds, enter the body’s circulation. Bioavailability is influenced by a variety of factors, including dose, the presence of other foods or substances, and interindividual differences in metabolism due to gut absorptive surface and commensal microbial populations.
Organic pigments that are found mainly in the chloroplasts of plants and are responsible for absorbing light. Plants use carotenoids to create energy and protection from harmful UV rays and animals commonly use carotenoids as a precursor for vitamin A.
A major contributing factor to aging, cellular senescence, and the development of cancer. Byproducts of both mitochondrial energy production and immune activity are major sources of DNA damage. Additionally, environmental stressors can increase this base level of damage. DNA damage can be mitigated by cellular repair processes; however, the effectiveness of these processes may be influenced by the availability of dietary minerals, such as magnesium, and other dietary components, which are needed for proper function of repair enzymes.
A circulating lipoprotein that picks up cholesterol in the arteries and deposits it in the liver for reprocessing or excretion. HDL is often referred to as the "good cholesterol."
A critical element of the body’s immune response. Inflammation occurs when the body is exposed to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. It is a protective response that involves immune cells, cell-signaling proteins, and pro-inflammatory factors. Acute inflammation occurs after minor injuries or infections and is characterized by local redness, swelling, or fever. Chronic inflammation occurs on the cellular level in response to toxins or other stressors and is often “invisible.” It plays a key role in the development of many chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
A substance produced in the brain. Norepinephrine acts as a hormone and neurotransmitter and is best known for its role in the body’s “fight or flight” response to stress. Its role as a neurotransmitter has been exploited as a molecular target for a class of drugs known as norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, which were developed for the purpose of treating disorders ranging from ADHD to narcolepsy and depression. Norepinephrine also plays a role in converting white adipose tissue into brown adipose tissue via an uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) mediated mechanism.
Distinctive structures comprised of short, repetitive sequences of DNA located on the ends of chromosomes. Telomeres form a protective “cap” – a sort of disposable buffer that gradually shortens with age – that prevents chromosomes from losing genes or sticking to other chromosomes during cell division. When the telomeres on a cell’s chromosomes get too short, the chromosome reaches a “critical length,” and the cell stops dividing (senescence) or dies (apoptosis). Telomeres are replenished by the enzyme telomerase, a reverse transcriptase.
Hear new content from Rhonda on The Aliquot, our member's only podcast

Listen in on our regularly curated interview segments called "Aliquots" released every week on our premium podcast The Aliquot. Aliquots come in two flavors: features and mashups.
- Hours of deep dive on topics like fasting, sauna, child development surfaced from our enormous collection of members-only Q&A episodes.
- Important conversational highlights from our interviews with extra commentary and value. Short but salient.
Omega-3 News
- Omega-3s protect the heart and muscles against damage incurred during endurance running.
- BDNF emerges as a critical marker of omega-3 fatty acid levels in the brain.
- Study shows people with a high omega-3 DHA level in their blood are at 49% lower risk of Alzheimer’s
- High-dose 2.4g EPA/DHA omega-3 in third trimester of pregnancy decreased the risk of wheeze & asthma during first 5 years of child's life by 54%
- Eating fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids reduces risk of asthma in some children.

























I haven’t been getting much omega 3 in my diet. I know that plasma levels of omega 3 respond rather rapidly to increased intakes of omega 3 . But how rapidly after taking more omega 3 in the diet and or supplementing with krill oil would it take to correct any shortage in the brain. Would you expect significant changes in brain omega 3 levels after a week or 2 of higher intake or would this take many months.
Rhonda, I’m a 59-yo Iraq war vet who’s seen the light about supplementation thanks to you and your peers who specialize in longevity. Thanks for your work!
The last piece of my supplementation puzzle is omega-3 supplementation. I’ve spent easily 20 hours trying to figure out why you still supplement with both triglyceride & phospholipid forms of omega-3. I’m doing the same - because you do - lol…
Set me (and countless others, I’m sure) straight on the why? Thanks so much!
Czissman, I heard Rhonda say in her 9/29/14 podcast about DHA and Krill Oil that she takes both forms basically as an insurance policy because we don’t know everything about Omega 3s and how the body uses them. From what I gathered from Rhonda, if your supplement budget is limited, it’s better spent on phospholipids.
Curious what you think of viva Labs aka krilloil.com - or what you take as a preferred supp. (I use their stuff now, and I feel great taking it in conjunction with lemon cod liver). You may not be able to comment on this, but maybe you have a link handy that compares available krill oils. IDK. Love your content! (supporter on Patreon.) - Kevin